The IoT industry is booming thanks to its versatility and application in various industries. In fact, globally, the IoT market is expected to grow to over $561 billion by 2022. An IoT (Internet of Thing) is a connected, smart device capable of connecting to and sharing data with another device, often a smartphone.
In general, we can see the growth of the IoT’s as a result of three arenas: the smart home, the smart building, and the smart city.
Each of these three arenas has potential to foster the growth of the industry. Despite its potential, the IoT industry is currently plagued by a significant problem. Every year, the industry spends millions on the recall of defective devices that often result from digital bugs. In fact, between 2018 and 2022, the IoT industry is set to spend $10 billion to recall defective devices caused by software bugs.
To avoid these losses as well as damage to brand image, it is absolutely necessary to perform quality assurance (QA) testing before any IoT is launched.
Nonetheless, there are a number of challenges that make testing IoT’s difficult. Below, we illustrate three major challenges.
3 IoT Testing Challenges
1) Test Coverage
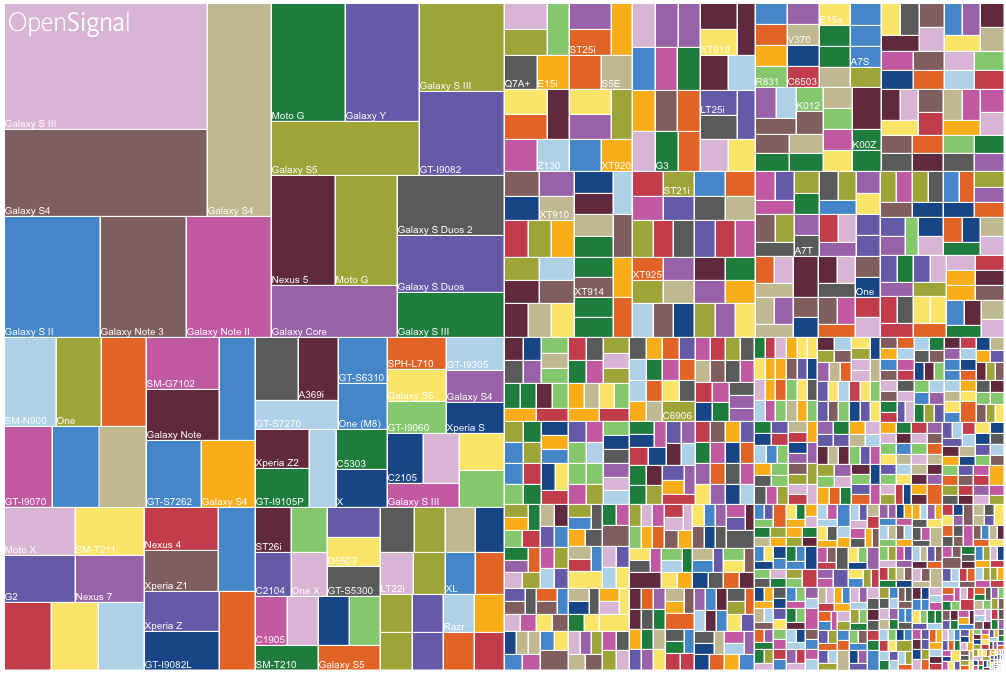
Due to fragmentation, or the diversity of the smartphone market based on brand, model, OS, versions of the OS, screen size, and other elements, it is a challenge to build an IoT that can work perfectly across countless devices.
Each tile represents a specific smartphone model and version of the Android OS. The size of the tile corresponds to its market share as of 2015.
However, the commercial success of an IoT depends on this. Therefore, it is essential to test IoT’s across dozens of devices to verify their quality and uncover bugs that can hinder functions and the user experience.
For many companies without a library of relevant testing devices, the effectiveness of a QA campaign can be watered down by an inadequate test coverage.
2) Test Diversity
Testing an IoT involves more just testing the actual device. It also includes testing its mobile application on a variety of devices to uncover bugs that can lead to recalls, hurt brand image, or erode consumer confidence.
While some test methods can focus on evaluating key functions, others can be better utilized to assess other important aspects like UX or accessibility. Without the right testing expertise, it can extremely difficult to plan, design, and execute a proper test.
3) IoT Stability
The key to any IoT is its ability to connect to other devices via a Bluetooth connection and/or a wifi network. Connecting and staying connected to another device or network is complex. Connection issues can rendre an IoT useless if it prevented from communicating and sharing data.
To avoid these difficulties, it is essential to test the ability of an IoT to connect to other devices. The type of connection used in a test should reflect the full capabilities of the IoT device. Furthermore, testing the connection should be done over a large amount of time as well as with a variety of devices with different bluetooth and wifi configurations.
IoT Testing Advice
While the challenges are real, they are steps you can take to execute a proper test for IoT’s. Here to explain these suggestions, is Isabelle, a StarDust project manager specially trained in QA for IoT’s.
Conclusion
The future of IoT’s will depend on confidence of consumers, which makes it vital for companies to launch high-quality IoT’s and software. Key to this endeavor is QA testing to uncover and correct any defects or bugs before a product hits the market.
With various clients in the IoT industry and a library of over 3,000 testing configurations, StarDust has the experiences, resources, and know-how required to plan, design, and execute proper QA campaigns for IoT’s. Learn more about our experience testing IoT’s by downloading a client testimonial for a major IoT manufacturer.