Smartphones with foldable displays, or foldables, and dual-screen mobile devices demonstrate the challenge that screen fragmentation creates for mobile app developers.
If smartphones were a community, it would be one of the most diverse. On one level, smartphones are produced by dozens of brands that each create various models every year supporting different hardware and software.
The screen dimensions, resolutions, and other characteristics are just some of the hardware aspects that can differ greatly between smartphones. For an example, look no further than to Apple’s line of iPhones which support different screen sizes, resolutions, and characteristics such as the notch.
Case Study: The Impact of the iPhone X

For developers, building apps that work perfectly across countless configurations is extremely difficult. It is not uncommon for an app to be affected by bugs that can be tied to a specific configuration such as screen size, OS version, browser version, etc., hindering functions and the user experience.
With the rise of foldables and dual-screen mobiles, screen fragmentation is becoming more complicated.
Why App Quality is Important
Apps play a major role in the lives and digital experiences of smartphone users. On average, people spend 3.1 hours consuming media on their smartphones. 74% of that time or 2.3 hours is spent on mobile apps. More importantly, around 50% of all Internet traffic comes from mobile apps.
As such, the commercial success of foldables or dual-screen smartphones will be affected by the quality of mobile applications. The unique screen characteristics and features of these smartphones can present challenges for app developers that, if unresolved, can result in bugs that constantly affect the user's experience.
Foldables or dual-screen mobiles that are plagued by bug-prone apps due screen fragmentation will ultimately generate negative reviews or complaints. Although unfair, these disappointing experiences will be associated more with the quality of the phone than any particular app.
As a result, it is essential to update or build new mobile apps to account for the unique characteristics and functions that set foldables or dual-screen mobiles apart.
Updating Apps for Foldables and Dual-Screen Smartphones
Starting with Android Pie, Google has provided developers with a mobile operating system that enables apps to transition between the different display modes. Android Pie also makes it possible for users to run two apps on their screen at the same time. With Android 10, users can supports 3 apps at a time.
App developers face the important task of developing new apps or updating existing ones that can support foldables, dual-screen phones, and support the mainstream screen dimensions.
It is also important to note that challenges presented by foldables and dual-screen devices place further emphasis on the importance of quality assurance (QA) testing.
QA Testing Foldables and Dual-Screen Phones
The key to testing apps on foldables and dual-screen smartphones is testing the full range of functions that apps offer while also accounting for the ways in which people will use these new smartphones.
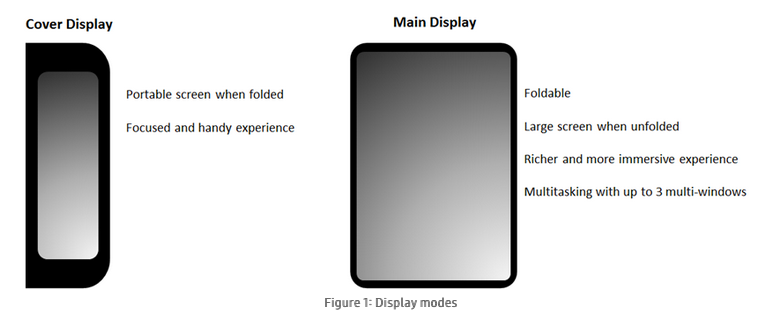
First, functional tests and more user experience focused tests must be carried out to assess the quality of the mobile app across the cover display mode and main display mode.
Test cases should take into account the specific functions that will be available when using the cover display versus the main display.
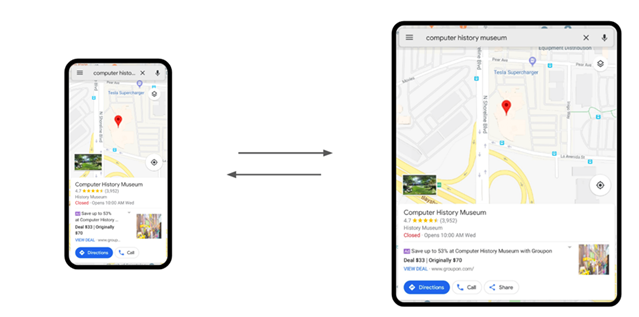
Second, it is important for QA teams to validate the app's continuity to ensure the mobile app operate seamlessly when users either expand or reduce the size of the screen. It is also vital to verify that users can transition between display modes without experiencing any lags or other anomalies that can hinder the app’s functions or UI.
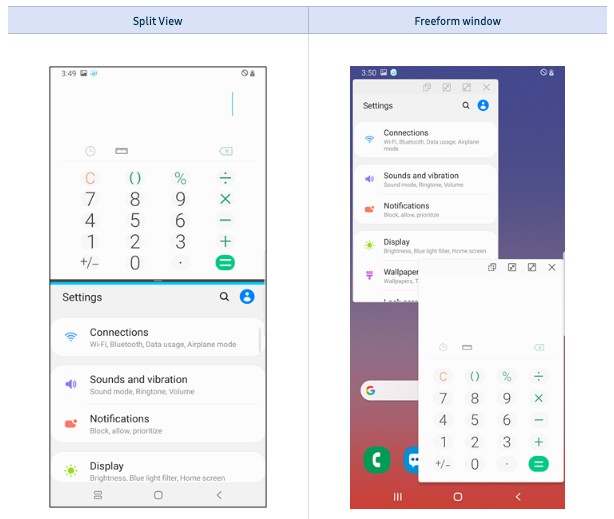
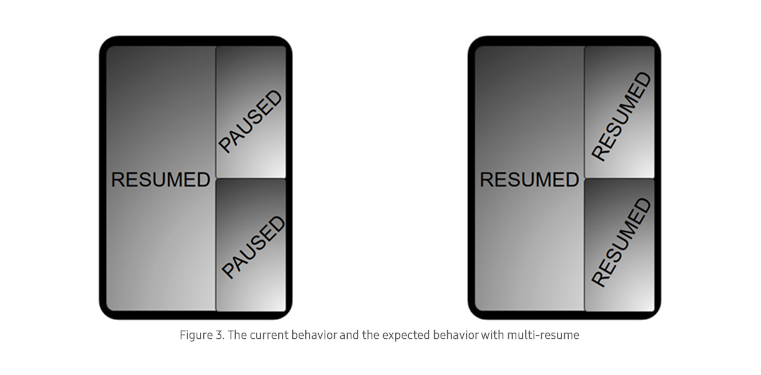
Third, tests should evaluate the app using the multi-window features offered by Android. This includes the Split View, Freeform window, and Multi-Resume functions.
Under Android's Split View, users can divide their screen to run multiple apps at the same time. The Freeform function allows to do the same by shrinking the size of the app window. In both cases, test cases need to validate the app while used in Split View and Freeform window.
As previously mentioned, Android 10 enables users to open and run up to three apps simultaneously. Test campaigns use validate an app’s UI and functions while used with the phone's multi-resume function.
To learn more about testing foldables or dual-screen smartphones, please do not hesitate to contact us. In addition, we invite you to discover our white paper: How and Why to Test in the Era of Digital Transformation.